How to use read, readline, and readlines (python) Read a csv file |
|||||||
・pip ・MeCab ・class ・pickle ・read/readline ・asfarray ・digitize ・expit ・linalg.solve ・meshgrid ・mgrid ・ndmin ・pad ・poly1d ・polyfit ・prod ・shape ・figure ・pcolormesh ・scatter ・BCELoss, MSELoss ・device ・Embedding ・TensorDataset, Dataloader ・RNN, LSTM ・SVC ・GaussianNB ・interpolate ・postscript ・image display ・frame, grid ・Crop Image ・linear interpolation ・Hysteresis switch ・Square/Triangle wave ・CartPole-v0 ・1 of K Coding |
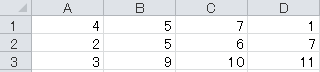
■Description
with open("test.csv", "r") as file: # r means read only
with open("test.csv", "r") as file:
with open("test.csv", "r") as file:
data[1].split(',') # split separates data with any character.
|
|
|||||