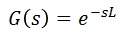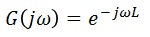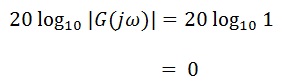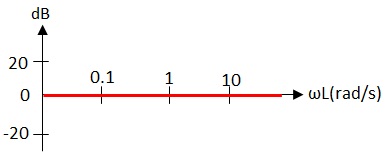Transfer function of dead-time system (all-pass filter), Bode plot |
|||||||||||
・First-order delay system ・Transfer function ・Bode plot ・secondary delay system ・Transfer function ・Bode plot ・Butterworth filter ・Bessel filter ・Lagged derivative ・Transfer function ・Pade approximation |
・In Japanese
■Transfer function of the dead-time system
As below. L:Dead-time.
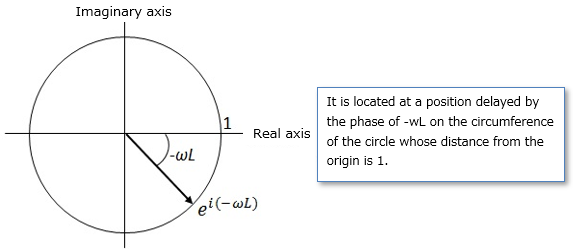
■Representation of dead-time systems on the complex plane
The above equation can be represented by Euler's formula and is located on the circle at distance 1 from the origin in the complex plane. ■Gain characteristics of dead-time system
Using the decibels formula, we get: ■Phase Characteristics of dead-time Systems
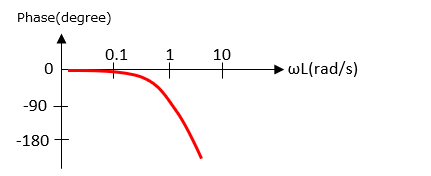
As ωL increases, the phase lags. ■Simulation results of dead-time system
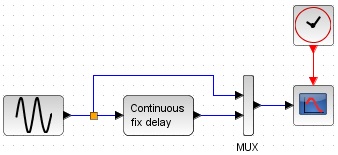
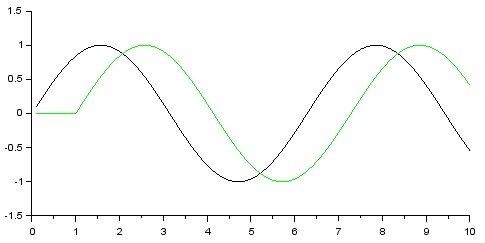
As below. Since the dead time cannot be represented by a normal transfer function block, we use a delay block.
|
|
|||||||||