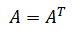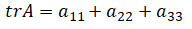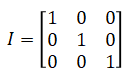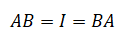What is a matrix? Purpose and types of matrices |
||||
・Exponential function ・Arctan, tanh ・Matrix multiplication ・Transposed matrix ・Fourier transform ・Fast Fourier Transform ・Matrix derivative ・Manhattan/Euclidean distance ・Centroid ・Vertical bar ・Gaussian integral ・Cosine similarity ・summation Σ, product Π ・Decibel[dB] ・Numerical Differention ・Induction,deduction,abduction ・Spline curve ・Lagrange's Method of Undetermined Multipliers ・Purpose of the matrix ・Proof by contradiction ・Vector field |
■What is a matrix?
A matrix is an arrangement of numbers or variables.
For example, the following is a matrix with 2 rows and 2 columns.
Each number in a matrix is called an element or component. ■Purpose and examples of using matrices
The purpose of using matrices is to make even complex calculations easier to understand by integrating numerical values and formulas into one matrix.
The following are examples of how matrices are used.
・Solving simultaneous equations
■Types of matrices
<Square matrix>
|
|
||