Difference between induction, deduction and abduction |
||||
・Exponential function ・Arctan, tanh ・Matrix multiplication ・Transposed matrix ・Fourier transform ・Fast Fourier Transform ・Matrix derivative ・Manhattan/Euclidean distance ・Centroid ・Vertical bar ・Gaussian integral ・Cosine similarity ・summation Σ, product Π ・Decibel[dB] ・Numerical Differention ・Induction,deduction,abduction ・Spline curve ・Lagrange's Method of Undetermined Multipliers ・Purpose of the matrix ・Proof by contradiction ・Vector field |
■Difference between induction, deduction and abduction
Induction is a method of finding common denominators from multiple individual phenomena and deriving general principles. For example:
① Last Friday's dinner was curry (individual phenomena)
The deductive method infers individual events from general principles. A typical example of deductive reasoning is syllogism. For example:
① Curry is served for dinner every Friday (in principle)
① Curry is served for dinner every Friday (in principle)
<Summary of differences between induction, deduction, and abduction>
■Mathematical induction
Mathematical induction is the application of induction to mathematical phenomena, and the following are typical patterns:
① Phenomena X holds true when natural number n=1
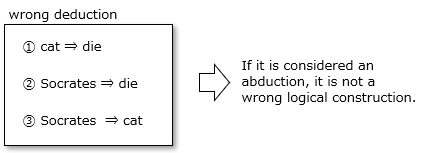
■An example where the deductive method does not hold
The following is a famous example of a wrong deduction method, but if you think of it as an abduction, it is not a wrong logical construction. (Whether the hypothesis is correct or not is a different matter)
|
|
||