How a DC-DC converter works |
||||
・Freewheeling Diode ・Alternating current ・Termination resistor ・CPU, LSI, IC, ASIC ・Adders, Subtractors ・H-bridge circuit ・Motor type ・Inverter ・AC-DC converter ・DC-DC converter ・Transformer ・ROM, RAM, register, cash ・open/short circuit failures ・Low-side, high-side driver ・Mechanism of electric shock ・Zener diode ・Rectifier circuit ・Pull up/down resistor ・Joule heat ・Solenoid valves, relays ・Comparator ・Switch Type ・Analog-to-Digital Conversion ・Clock generator ・Surge Current ・Clarke transformation ・d-q, Park transformation ・Sine Wave Generation |
・In Japanese
■What is a DC-DC converter?
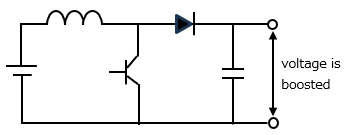
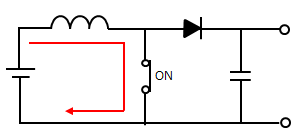
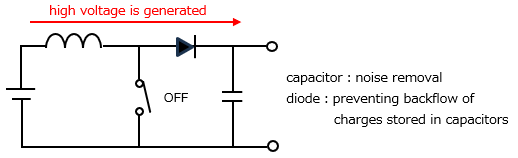
A DC-DC converter is a device that has the ability to step up or step down direct current. It mainly consists of a transistor and a coil, and is a type of switching regulator.
<Step-up DC-DC converter>
as below. <Step-down DC-DC converter>
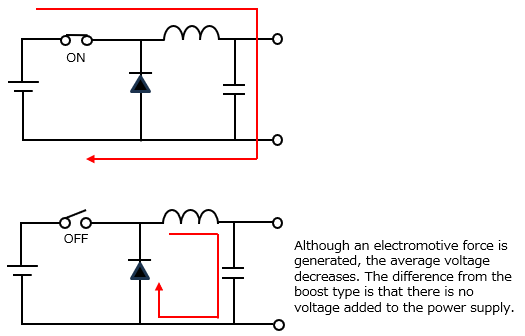
The step-down type circuit is as follows. The individual roles of the coil, capacitor, and diode are the same as in a step-up DC-DC converter, but the overall function changes just by changing the circuit.
When the switch is turned off, the coil momentarily generates a high electromotive force, but the average voltage drops.
The difference from a step-up DC-DC converter is whether or not the voltage from the power supply is applied.
|
|
||