I-PD type control |
|||||||||||
・First-order delay + P controll ・2nd order delay + PID
|
・In Japanese
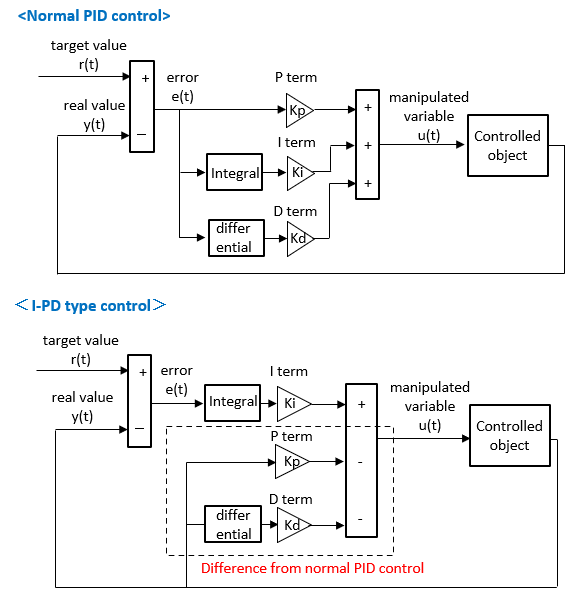
■What is an I-PD type control
In PID control, when the target value changes significantly due to the derivative term or proportional term, a large change in the manipulated variable is called a kick.
Here, I will explain I-PD type control, which is one of the techniques for suppressing kicks.
A similar control is called PI-D type control.
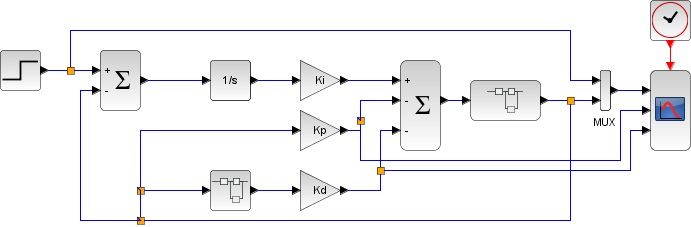
■I-PD type control design
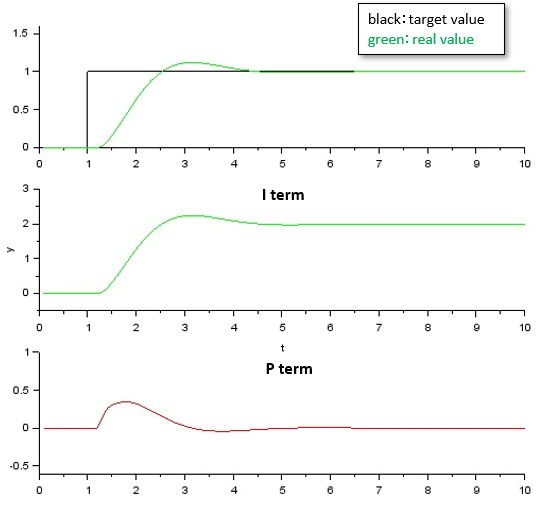
The design result in Scilab is as follows. Click here for the controlled object and the contents of the differentiator <Disadvantages of I-PD type control>
With I-PD type control, there is no sudden change (kick) in the amount of operation, but there is a disadvantage of slow response.
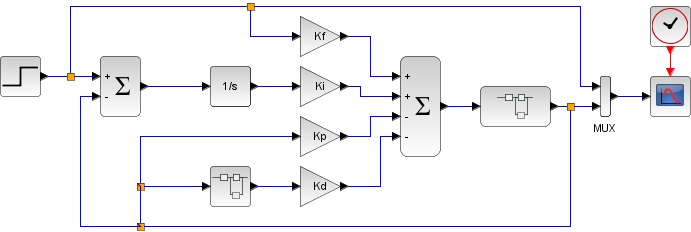
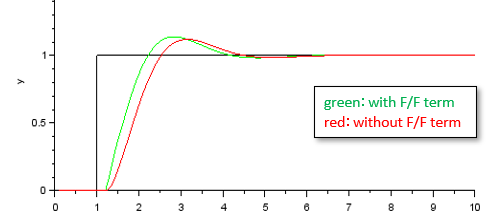
The following methods are used to improve responsiveness. ■Feed forward and I-PD type control
To improve responsiveness, a gain is given to the target value as follows. This is the effect of feedforward.
|
|
|||||||||