Differential Signaling Mechanism |
|||||||
・CAN,LIN communication ・SENT communication ・USB Communication ・Ethernet ・SPI Communication ・Parity, Check sum, CRC ・Data transfer speed ・Clock synchronous, Asynchronous methods ・Differential Signaling ・PLC, Superimposed Circuit ・Single/multi-master system ・Message authentication, Digital signature |
・In Japanese
■What is Differential Signaling?
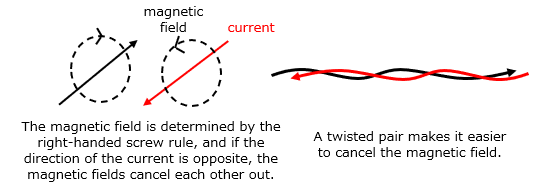
Differential signaling is a serial communication method that uses two signal lines to increase noise resistance, resulting in high-speed communication.
This method can coexist with unidirectional communication, and even if it is unidirectional communication, it uses two signal lines.
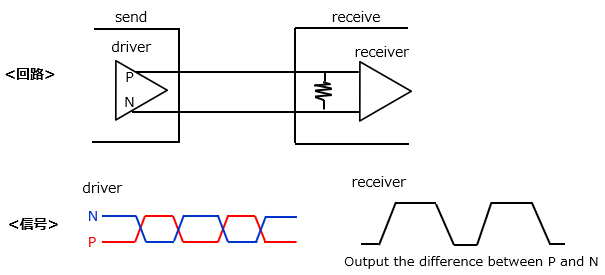
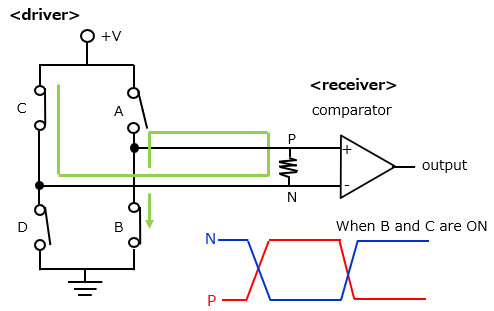
The circuit diagram and signal behavior are shown below. Output P is positive and the output is high, and N is negative and the output is low.
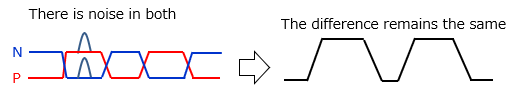
Differential signaling is resistant to noise for two reasons.
One is that when noise is added to the transmission path, the noise is applied equally to both the P side and the N side, and the difference remains the same. ■Differential signaling working mechanism
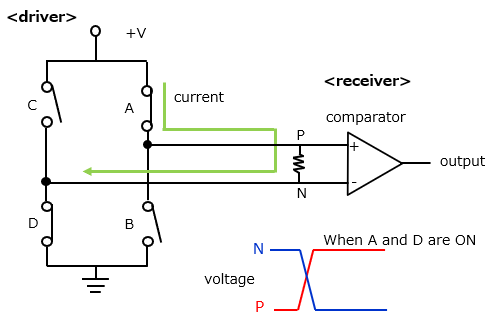
The receiver uses a comparator and the driver uses an H-bridge circuit.
This shows the current flow when switches A and D are turned on. At this time, the voltage level is High for P and Low for N.
|
|
|||||