How message authentication and digital signatures work |
|||||||
・CAN,LIN communication ・SENT communication ・USB Communication ・Ethernet ・SPI Communication ・Parity, Check sum, CRC ・Data transfer speed ・Clock synchronous, Asynchronous methods ・Differential Signaling ・PLC, Superimposed Circuit ・Single/multi-master system ・Message authentication, Digital signature |
・In Japanese
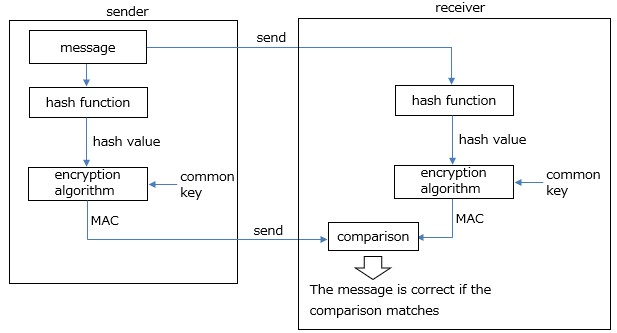
■What is message authentication?
Message authentication is one of the encryption technologies for checking whether a message has been tampered with, and a message authentication code (MAC) is a ciphertext.
■What is a digital signature?
A digital signature is an encryption technique that verifies that a message has been tampered with and whose message it is. ■Differences between message authentication and digital signatures
Message authentication can confirm that the message has not been tampered with, but it does not guarantee who sent it, but digital signatures can tell who sent it.
You may think that message authentication is not necessary, but the advantage of message authentication is that the calculation speed is faster than that of digital signatures (due to the difference between public key cryptography and common key cryptography).
Therefore, if you don't need to guarantee who sent the message, message authentication should be fine.
|
|
|||||